Disks, Shared Drives, ISO booting and Resizing
Everyday Tools
qqX will automatically run disk health checks in the background and alert you if there are problems.
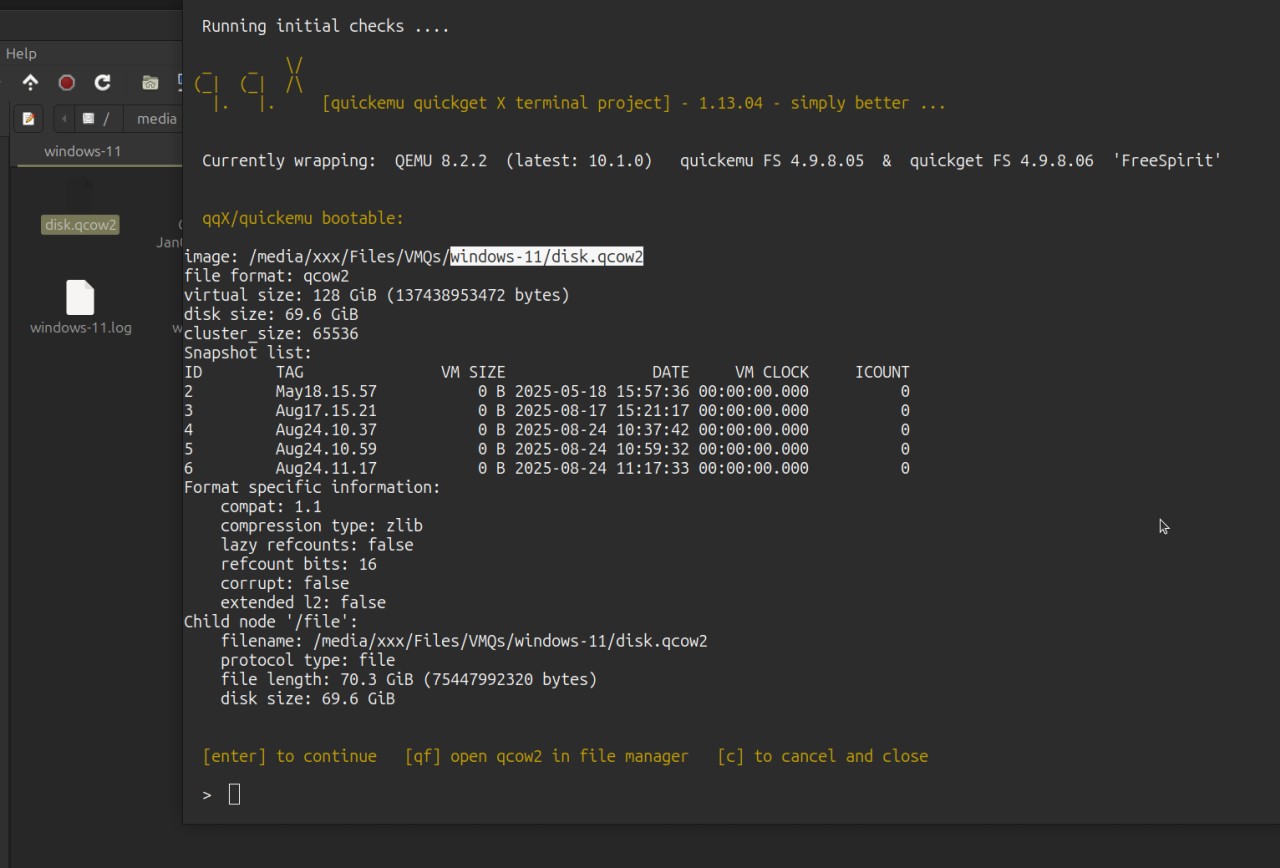
You are also able to mount and view qcow2 virtual machine drives using the host's file manager
[qf] | [qqf] open a qcow2 drive in file manager [f] open VM folder
Click here to Google Auto-Translate these Screenshots
Right click to VIEW INSIDE any VM disk
SHARED and SECOND DRIVES
The standard Quickemu shared drive method normally works with the folder $HOME/Public
-
This has a neat desktop to desktop copy/paste feature for text and files
-
Allows a live and generally easy bi-directional access to the
Publicfolder
BUT
- It won't work with SDL, which is much faster and crisper, it only works with Spice.
- Windows guests will need the SPICE guest tools to be installed in the Windows VM
To improve usage of SDL, qqX takes things a stage further and allows you to create another type of Shared Drive:
- Open the [u] Utils menu:
[2c] create [2d] delete a second virtual hard-drive [3c] create [3m] unmount shared drive (guest boot)
-
Works in all display modes. May be used by all the VM's and may be accessed by the host.
-
qqX will normally auto-install the shared drive parameters for you, in the general settings file, and will enable auto-mount.
-
Stage by stage help is given on screen but this link to the translation shared drive help screens may assist.
-
Copy and paste should become supported as SDL 3 works its way through into the display systems ...
SECOND DRIVES are installed in much the same way.
These are focused at individual distros, so qqX will generate auto-mounting via the .conf file.
-
A Second drive is a quick way to expand an individual VM's storage.
-
The .conf file entry may be copied to other distros, to extend further sharing capabilities.
Partioning and formatting
Just like any new hard drive or disk, and just like when a distro is installed, we need to initialize things.
This should be carried out INSIDE a virtual machine or from a boot ISO.
- Use Gparted, Gnome Disks, or similar
You will need to install a partion table and will need to create and format at least one partition.
- To create the partition table using Gparted, select 'Devices' from the top menu. Normally select GPT.
For WINDOWS VMs, the drive should be created as GPT and formatted as NTFS.
-
Set up NTFS drives using a Linux OS and Gparted but optimize (defrag) the disk using Windows
-
See resize notes for mounting workarounds
MAC OS, older than and including 10.13 Mojave 2018 might need a flag IN THE .CONF FILE to stop possible drive conflicts.
-
Quickemu code has the following MacOs note: "VirtIO Block Media doesn't work in High Sierra (at all) or the Mojave (Recovery Image)" Development tests with Mojave show both a Shared NTFS and a Second APFS to be working.
-
Thus, SET MacLegacyDrive as ="true" to load Second Drive (& not Shared) as 'ide-hd' instead of 'virtio-blk-pci'
The Shared Drive will always load as 'virtio-blk-pci'
RESIZING
Ideally the Virtual Machine should have been allocated a generous size from the outset. But things aren't always that way ...
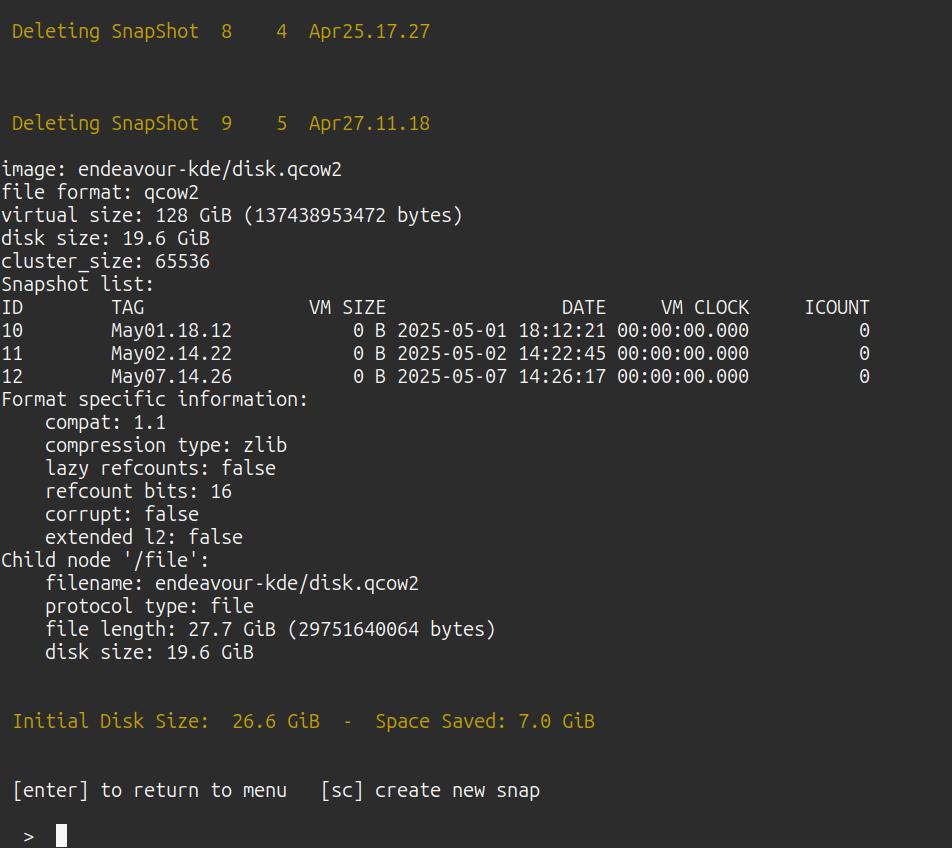
Select the VM in the normal way and open the Utils menu [u]
Use the [disk] option to resize. Stage by stage help will be given.
-
See this link to the disk resize translation help screens, and others.
-
Second drives should be followed up by adjustments using Gparted from inside the Linux VM.
Gparted will auto-detect the change in envelope size and auto offer to 'fix' things. KDE partition manager may not do this and will need the partition deleting in order to reach the new envelope size. This software is not always installed and may need to be added.
-
A workaround for KDE distros can be to copy the disks to a Gnome based distro VM folder, then mount them as Gnome second drives. Even a simple Live ISO is sufficient, as long as the .conf has the Drive added to it.
-
This workaround should function with main drives too, including Windows.
-
Or not. Sometimes only Windows will fix NTFS, even if Gparted has already done the main lifting. Windows has 'Check and repair' plus 'Defrag' and Trim functions that can fix things sometimes where others can't.
BOOTING from ISO's
-
An in-menu ISO boot is now possible from version 1.9.03
-
And a space saving shared Boot ISO option is now possible from 1.11.05 onwards
-
See the [iso] utility from the main menu.
By pressing the 'esc' key during initial boot, you can access the Tiano boot manager and boot from any 'live boot' ISO, such as the one from https://gparted.org/download.php
ACCESS
If your drives only have root access, the following commands can help give general user permissions:
sudo chown $USER:$USER "mounted-drive-name"
chmod 775 "mounted-drive-name"
Gnome Disks has a neat 'take ownership' option:
Transferring virtual machines
A method of converting VMs from or to lib-virt based environments, such as Gnome Boxes or Virt-Manager, is still a work in progress which is hoped to be resolved.